Exploring Holistic Healing: A Guide to Alternative Medicine Practices
In “Exploring Holistic Healing: A Guide to Alternative Medicine Practices,” readers are invited to delve into the world of alternative approaches to wellness. With a friendly tone and a focus on evidence-based information, this guide aims to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. By presenting a range of alternative medicine practices, readers can explore holistic healing and discover new paths to wellness. With the belief in the power of holistic healing, this guide provides reliable content to inspire and support holistic lifestyles.
I. Introduction to Alternative Medicine
A. What is alternative medicine?
Alternative medicine refers to a broad range of medical practices and treatment approaches that are not considered part of conventional or mainstream medicine. These practices often focus on promoting holistic healing, taking into account the physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects of an individual’s well-being.
B. History of alternative medicine
Alternative medicine has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Many ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Chinese, developed diverse healing traditions based on natural remedies, herbal medicine, and spiritual practices. These traditions and knowledge were passed down through generations and laid the foundation for many alternative medicine practices we see today.
C. Principles of alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is guided by several key principles. First and foremost, it emphasizes the belief that the body has an innate capacity for self-healing. It recognizes the interconnectedness of various aspects of human health and seeks to address the root causes of illness rather than just managing symptoms. Alternative medicine also emphasizes the importance of individualized care, recognizing that each person is unique and requires personalized approaches to promote well-being.
II. Types of Alternative Medicine Practices
A. Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a comprehensive medical system that originated in ancient China. It encompasses various practices, including acupuncture, herbal medicine, massage, dietary therapy, and exercise (such as tai chi and qigong). TCM is based on the concept of balancing the body’s vital energy, known as Qi, and maintaining the harmonious flow of Qi through meridians or pathways in the body.
B. Ayurveda
Ayurveda is a holistic healing system that originated in India over 5,000 years ago. It focuses on balancing the three fundamental energies, known as doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), to achieve optimal health. Ayurvedic practices include herbal remedies, dietary guidelines, yoga and meditation, detoxification procedures, and lifestyle recommendations tailored to an individual’s unique constitution.
C. Naturopathy
Naturopathy is a system of healthcare that emphasizes the body’s inherent ability to heal itself and promotes wellness through natural therapies. Naturopathic doctors focus on identifying and treating the underlying causes of disease, rather than merely suppressing symptoms. Naturopathic treatments may include dietary modifications, nutritional supplements, botanical medicine, homeopathy, hydrotherapy, and lifestyle counseling.
D. Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a system of alternative medicine that is based on the principle of “like cures like.” It involves using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s self-healing mechanisms. Homeopathic remedies are made from plant, mineral, or animal sources and are selected based on an individual’s unique symptoms and constitution. Homeopathy aims to treat the whole person rather than focusing solely on the physical symptoms of an illness.
E. Chiropractic
Chiropractic is a healthcare discipline that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system, particularly the spine. Chiropractors use manual adjustments and manipulations to restore proper alignment and function of the spine, which can have a positive impact on overall health. Chiropractic care also encompasses other therapeutic approaches, such as exercise, nutrition, and lifestyle recommendations.
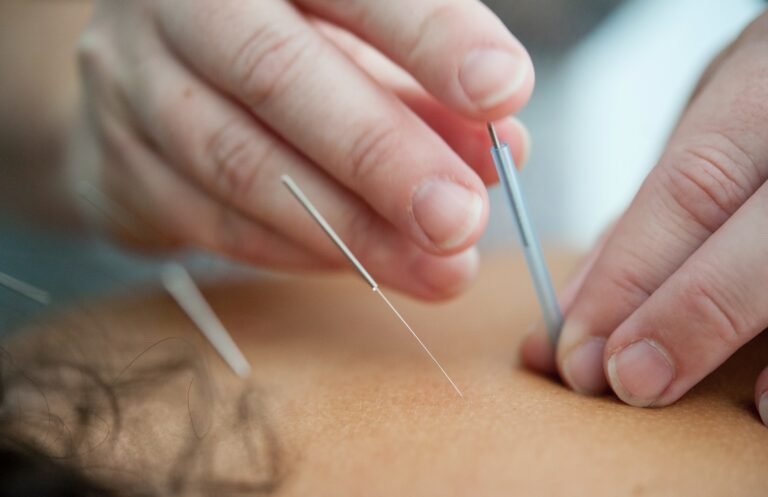
F. Acupuncture
acupuncture is a practice rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to regulate the flow of Qi, the body’s vital energy, and restore balance in the body. Acupuncture is widely used to alleviate pain, promote relaxation, and address a range of physical and emotional conditions.
G. Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine, also known as botanical medicine, utilizes plants and plant extracts for medicinal purposes. Different herbs and their active compounds are utilized to address specific health issues. Herbal medicines can be taken internally in the form of teas, capsules, or tinctures, or applied topically in the form of creams or ointments. The use of herbs for healing dates back to ancient times and is a central component of many traditional healing systems worldwide.
H. Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy is a practice that involves the use of essential oils derived from plants to promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being. These concentrated plant extracts can be inhaled, applied topically, or used in baths or diffusers. Aromatherapy is often used as a complementary therapy alongside other alternative medicine practices to enhance relaxation, relieve stress, and promote a sense of balance and harmony.
I. Reiki
Reiki is a Japanese healing technique that involves the laying on of hands to channel energy and promote healing. Practitioners believe that they can transfer universal life energy to the recipient, addressing imbalances in the body’s energy system and promoting overall well-being. Reiki is often used as a complementary therapy to reduce stress, promote relaxation, and support the body’s natural healing processes.
J. Reflexology
Reflexology is a therapeutic practice that involves applying pressure to specific areas of the feet, hands, or ears, which are believed to correspond to different organs and systems in the body. Reflexologists use their hands, fingers, and thumbs to stimulate these reflex points, aiming to restore balance and promote healing throughout the body. Reflexology is commonly used to relieve tension, improve circulation, and support overall well-being.

III. Traditional Chinese Medicine
A. Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a comprehensive medical system that has evolved over thousands of years in China. It is rooted in the philosophy that the human body is a complex and interconnected system, and maintaining the balance of vital energy, or Qi, is crucial for health and well-being. TCM encompasses a wide range of practices, including acupuncture, herbal medicine, massage, dietary therapy, and exercise, such as tai chi and qigong.
B. Traditional Chinese Medicine Techniques
In TCM, various techniques are employed to restore the balance and flow of Qi in the body. These include acupuncture, which involves the insertion of thin needles at specific points along the body’s meridians to stimulate Qi circulation and promote healing. Herbal medicine is another key technique in TCM, using specific herbs or combinations of herbs to address imbalances or ailments. Additionally, TCM incorporates massage techniques, such as Tui Na, to stimulate acupoints and meridians, as well as dietary therapy and exercises like tai chi and qigong to support overall well-being.
C. Acupuncture in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Acupuncture is one of the most well-known practices within TCM. It is based on the belief that when Qi flows freely through the body along the meridians, there is balance and health, but when the flow is disrupted, it can lead to illness. Acupuncture aims to restore the flow of Qi by inserting thin, sterile needles at specific points along the meridians. These points are carefully chosen based on the individual’s diagnosis and specific health concerns. Acupuncture is often used to address a wide range of conditions, including pain, digestive disorders, emotional imbalances, and fertility issues.
D. Herbal Medicine in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Herbal medicine is a fundamental part of TCM and involves the use of specific herbs or herbal combinations to address imbalances and promote healing. TCM herbal formulas are carefully prescribed based on the individual’s diagnosis, symptoms, and constitution. These formulas may include a variety of herbs, each with its unique properties and functions, working synergistically to restore balance and support the body’s natural healing processes. TCM herbal medicine can be taken in the form of teas, capsules, powders, or topical applications, and is commonly used to address a wide range of conditions, including allergies, insomnia, digestive issues, and hormonal imbalances.
IV. Ayurveda
A. Overview of Ayurveda
Ayurveda, which means “knowledge of life” in Sanskrit, is a holistic healing system that originated in India thousands of years ago. It is based on the belief that each individual is unique and that there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to healing. Ayurveda seeks to create balance in the body, mind, and spirit through a combination of lifestyle practices, dietary guidelines, herbal remedies, yoga and meditation, detoxification procedures, and personalized recommendations based on an individual’s dosha, or energy constitution.
B. Components of Ayurveda
Ayurveda recognizes the interconnectedness of the body, mind, and spirit and focuses on promoting balance and harmony in all aspects of life. It comprises three main components: doshas, dhatus, and malas. Doshas are the three fundamental energies – Vata, Pitta, and Kapha – which govern various physiological and psychological processes in the body. Dhatus refer to the seven bodily tissues, including plasma, blood, muscles, and reproductive tissues. Malas are the waste products of the body, such as urine, feces, and sweat.
C. Ayurvedic Practices
Ayurveda encompasses various practices aimed at creating balance and harmony within the body. These include dietary guidelines, which emphasize consuming fresh, seasonal, and organic foods that are tailored to an individual’s dosha. Lifestyle recommendations promote the importance of regular sleep patterns, stress management, and daily routines. Ayurvedic treatments may also include herbal remedies, massage therapies, yoga and meditation practices, detoxification procedures, and rejuvenation therapies known as Panchakarma.
D. Ayurvedic Diet
The Ayurvedic diet is an essential aspect of Ayurveda and emphasizes the consumption of foods that are considered balancing for an individual’s dosha. Each dosha has specific dietary guidelines to support overall well-being. For example, individuals with a Vata dosha may benefit from warm, nourishing foods, while those with a Pitta dosha may thrive on cooling, hydrating foods. Kapha types may benefit from lighter, drier foods. The Ayurvedic diet also promotes mindful eating, incorporating all six tastes, and avoiding processed foods and artificial additives.
E. Ayurvedic Herbs and Supplements
Ayurvedic herbs and supplements play a significant role in restoring balance and promoting healing. These herbs are carefully selected based on an individual’s dosha and specific health concerns. Ayurvedic herbal remedies can be used to address various conditions, ranging from digestive issues and hormonal imbalances to respiratory problems and skin conditions. Common Ayurvedic herbs include ashwagandha, turmeric, triphala, brahmi, and ginger. Ayurvedic supplements may come in the form of tablets, powders, or liquid extracts, and are typically prescribed by an Ayurvedic practitioner.

V. Naturopathy
A. Principles of Naturopathy
Naturopathy is a system of healthcare that focuses on supporting and stimulating the body’s natural healing processes. It is guided by six principles: the healing power of nature, identifying and treating the root cause of illness, treating the whole person, focusing on prevention, doctor as a teacher, and promoting wellness. Naturopathic doctors aim to address the underlying causes of disease rather than merely managing symptoms and utilize natural therapies to support the body’s innate healing abilities.
B. Naturopathic Techniques
Naturopathic doctors employ a wide range of natural techniques to promote health and well-being. These may include dietary modifications, such as personalized nutrition plans or therapeutic diets to address nutritional deficiencies or food sensitivities. Nutritional supplements, such as vitamins, minerals, and herbal preparations, may also be recommended to support specific health goals. Other naturopathic techniques can include physical medicine, such as chiropractic adjustments or massage therapy, hydrotherapy, acupuncture, and mind-body therapies like mindfulness and stress management techniques.
C. Naturopathic Treatments
Naturopathic treatments are individualized and aim to address the root cause of an individual’s health concerns. Naturopathic doctors may utilize a combination of therapies to support the body’s natural healing abilities. These treatments can include herbal medicine, homeopathy, hydrotherapy, physical medicine techniques like spinal adjustments or therapeutic massage, counseling and lifestyle modifications, as well as mind-body therapies such as meditation or biofeedback. The specific combination of treatments will vary based on the individual’s unique needs and health goals.
D. Benefits and Risks of Naturopathy
Naturopathy offers several potential benefits for individuals seeking a holistic approach to their health. The emphasis on treating the root cause of illness and supporting the body’s natural healing processes can lead to long-term improvements in overall health and well-being. Naturopathic treatments also often have fewer side effects compared to conventional pharmaceutical medications. However, it’s important to note that naturopathy is not a replacement for conventional medical care, especially in cases of acute or severe conditions. It’s essential to work with a qualified naturopathic doctor and maintain open communication with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive and safe care.
VI. Homeopathy
A. Introduction to Homeopathy
Homeopathy is a system of alternative medicine founded by Samuel Hahnemann in the late 18th century. It is based on the principle of “like cures like,” meaning that a substance that can cause symptoms in a healthy person can be used in a highly diluted form to stimulate the body’s self-healing mechanisms and treat similar symptoms in an individual who is unwell. Homeopathy considers the whole person and aims to address the underlying causes of illness rather than merely suppressing symptoms.
B. Homeopathic Remedies
Homeopathic remedies are prepared using a process called potentization, which involves diluting and succussing (shaking) a substance. The dilutions used in homeopathy are typically highly diluted, often to the point where little to no measurable amount of the original substance remains. These highly diluted remedies are thought to carry the energetic imprint of the original substance and stimulate the body’s healing response. Homeopathic remedies can be made from a wide range of sources, including plants, minerals, and animal substances.
C. Homeopathic Treatment Approach
Homeopathic treatment is individualized and tailored to each person’s unique symptoms and constitution. A homeopath considers the physical, mental, and emotional aspects of the individual, as well as the specific symptoms experienced. Homeopaths use a process called case-taking to gather detailed information about the person’s health history, symptoms, and overall well-being. Based on this information, the homeopath selects a homeopathic remedy that closely matches the individual’s symptoms and constitutional characteristics.
D. Evaluation of Homeopathy
Homeopathy continues to be a controversial topic in the medical community. Critics argue that the highly diluted nature of homeopathic remedies renders them ineffective, as they often contain no measurable amounts of the original substance. However, proponents of homeopathy argue that the energetic imprint of the remedy retains therapeutic properties. While scientific research on homeopathy has produced mixed results, some studies have shown positive effects, particularly in the treatment of certain conditions such as allergies and respiratory illnesses. It’s important for individuals considering homeopathy to consult with a qualified homeopath and maintain open communication with other healthcare providers.

VII. Chiropractic
A. What is Chiropractic?
Chiropractic is a healthcare discipline that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system, particularly the spine. Chiropractors believe that spinal misalignments, known as subluxations, can disrupt the normal functioning of the nervous system and lead to a range of health issues. Chiropractic care aims to restore proper alignment of the spine, helping the body heal itself and maintain optimal health.
B. Chiropractic Techniques
Chiropractors use a variety of techniques to restore spinal alignment and improve overall function. Manual spinal adjustments, or manipulations, are a hallmark of chiropractic care. These adjustments involve applying controlled, sudden force to specific joints of the spine or other parts of the body. This can help alleviate pain, improve joint mobility, and enhance the body’s ability to heal itself. Chiropractic techniques may also include mobilizations, soft tissue therapies, stretching exercises, and lifestyle counseling.
C. Conditions Treated by Chiropractic
Chiropractic care can be beneficial for a wide range of conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system and nervous system. It is commonly sought for back pain, neck pain, and headaches, but chiropractic care can also effectively treat conditions such as sciatica, joint pain, sports injuries, and carpal tunnel syndrome. Chiropractors take a holistic approach to care and may also address lifestyle factors, such as posture, ergonomics, and exercise, to promote long-term health and well-being.
D. Safety Considerations for Chiropractic Treatment
Chiropractic care is generally considered safe when performed by a licensed and experienced chiropractor. However, as with any form of healthcare, there are potential risks and safety considerations to be aware of. Rare but possible risks may include temporary soreness or discomfort after an adjustment, as well as rare instances of more serious complications, such as nerve damage or herniated discs. It is important to communicate openly with your chiropractor, disclose any relevant medical history, and follow their recommendations for care. Chiropractic care may not be appropriate for everyone, so it’s important to consult with your primary healthcare provider before pursuing chiropractic treatment.
VIII. Acupuncture
A. What is Acupuncture?
Acupuncture is a practice rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. It is based on the concept that the body has a network of channels, or meridians, through which energy, known as Qi, flows. When the flow of Qi is disrupted, it can lead to pain or disease. Acupuncture aims to restore the balance of Qi by stimulating specific points along the meridians.
B. Traditional Chinese Medicine Acupuncture vs. Western Acupuncture
There are two main approaches to acupuncture: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) acupuncture and Western acupuncture. TCM acupuncture follows the principles and techniques of Traditional Chinese Medicine, focusing on balancing the flow of Qi through meridians. Western acupuncture, on the other hand, has evolved within the framework of Western medicine and often incorporates scientific understandings of anatomy, physiology, and neurology to explain its effects. Both approaches can be effective, and the choice may depend on an individual’s personal preferences and the training of the practitioner.
C. How Acupuncture Works
The exact mechanisms by which acupuncture works are not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that acupuncture stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving substances. It may also affect the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which can influence mood and emotions. Additionally, acupuncture may modulate the activity of the autonomic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Current research is exploring the physiological effects of acupuncture and its potential benefits for a wide range of conditions.
D. Conditions Treated with Acupuncture
Acupuncture is commonly used to relieve pain, including musculoskeletal pain such as back pain, neck pain, and arthritis. It may also be effective in managing headaches, migraines, and menstrual cramps. Acupuncture has been studied for its potential benefits in various conditions, such as anxiety, depression, digestive disorders, respiratory conditions, and infertility. It is important to consult with a trained and experienced acupuncturist to determine the appropriate treatment plan and ensure the safety and efficacy of acupuncture for specific health concerns.

IX. Herbal Medicine
A. Introduction to Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine, also known as botanical medicine or phytotherapy, involves the use of plants and plant extracts for medicinal purposes. Plants have been used for healing purposes for thousands of years, and herbal medicine is a central component of many traditional healing systems worldwide. Herbal medicine utilizes the active compounds found in plants to promote healing, restore balance, and support overall well-being.
B. Common Herbs Used in Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine encompasses a vast array of plants with medicinal properties. Some commonly used herbs in herbal medicine include ginger, echinacea, ginkgo biloba, chamomile, garlic, turmeric, and lavender, among many others. Each herb has its unique properties and actions, which can be utilized to address specific health concerns. Herbal medicine recognizes the importance of individualized treatments, and an herbalist will consider an individual’s symptoms, constitution, and overall health when selecting appropriate herbs.
C. Herbal Preparations and Dosages
Herbal medicines can be prepared in various forms, depending on the desired effect and the herb being used. Common preparations include teas, infusions, tinctures, capsules, creams, ointments, and essential oils. The dosage and administration of herbal medicines are typically determined by an experienced herbalist or healthcare provider and may vary based on the individual’s age, weight, health status, and specific health concerns. It is important to follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider for guidance.
D. Safety and Efficacy of Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine has a long history of traditional use and can be a valuable adjunct or alternative to conventional medical treatments. However, it is essential to note that herbal medicines can still have side effects, interact with medications, or be contraindicated in certain individuals. It is important to consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider before using herbal medicines, particularly if you have pre-existing medical conditions, are taking medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding. Quality control and sourcing of herbs are also important considerations, and it is advisable to purchase herbal products from reputable sources.
XII. Reflexology
A. What is Reflexology?
Reflexology is a therapeutic practice that involves applying pressure to specific areas of the feet, hands, or ears, which are believed to correspond to different organs and systems in the body. Reflexologists believe that stimulating these reflex points can bring about physical and energetic changes in the corresponding body parts and promote overall well-being.
B. Reflexology Techniques
Reflexology techniques primarily involve the application of pressure with the hands, fingers, and thumbs to specific reflex points. Reflexologists may use various techniques, including finger-walking, thumb or finger pressure, rotational movement, and kneading. These techniques aim to release tension, improve circulation, and restore balance in the corresponding body parts.
C. Benefits of Reflexology
Reflexology is commonly sought for relaxation and stress relief. It can help promote a state of deep relaxation, which may help alleviate symptoms of stress, anxiety, and tension. Reflexology has also been reported to improve circulation, relieve pain, enhance sleep quality, and support overall well-being. Some individuals may find reflexology helpful for specific conditions, such as headaches, digestive disorders, respiratory conditions, and hormonal imbalances. However, it is important to note that reflexology is not intended to replace medical treatment, and individuals should consult with their healthcare provider for any medical concerns.
D. Reflexology and Pain Management
Reflexology is often used as a complementary therapy for pain management. By stimulating reflex points on the feet, hands, or ears, reflexology may help alleviate pain and discomfort in corresponding areas of the body. Reflexology can be beneficial for conditions such as chronic pain, musculoskeletal pain, migraines, and menstrual pain. It is important to work with a qualified reflexologist and maintain open communication with other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive and safe care when using reflexology for pain management.
Alternative medicine practices offer a unique and holistic approach to health and well-being. From Traditional Chinese Medicine to reflexology, each practice brings its unique principles, techniques, and benefits. By exploring alternative medicine, individuals can empower themselves to make informed decisions about their health and explore diverse approaches to healing. Whether seeking relief from pain, managing chronic conditions, or promoting overall wellness, alternative medicine practices can provide valuable options for individuals looking to enhance their well-being.